Proteins (10)
id: ivory-mole-clay
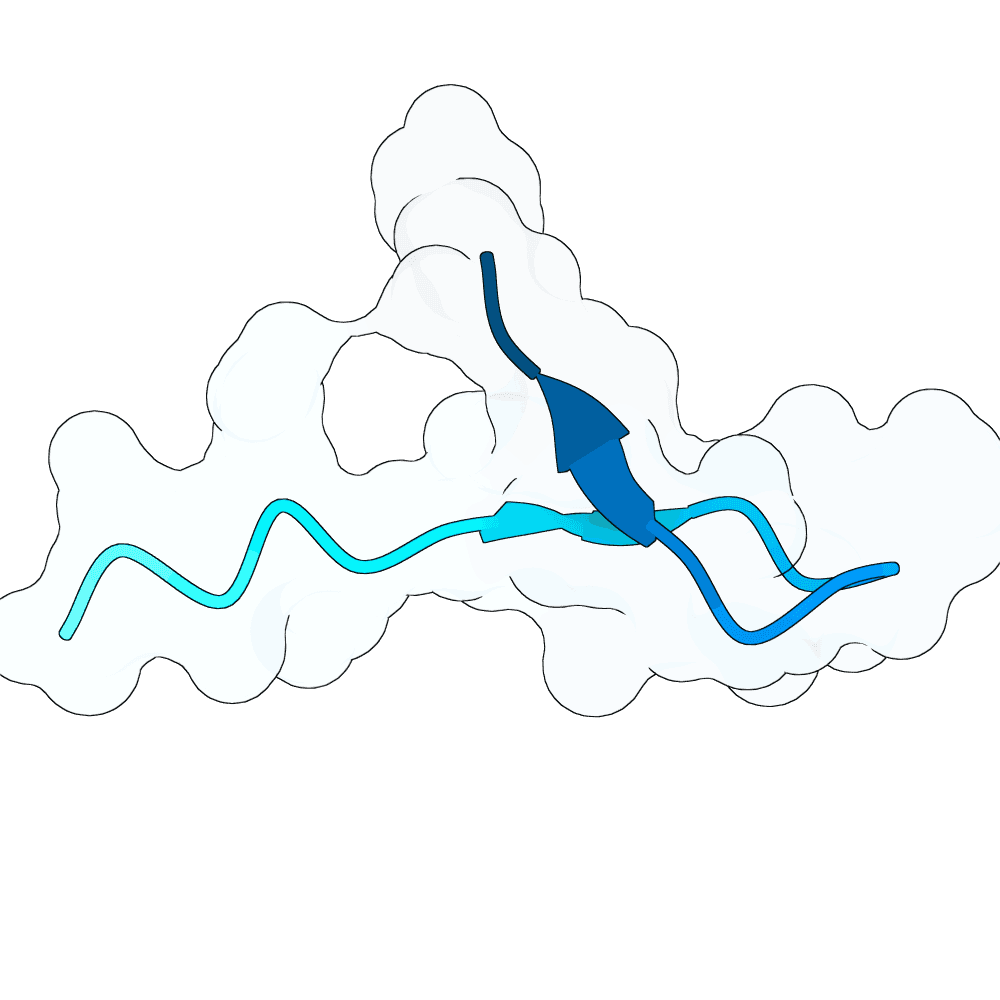
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.67
71.52
--
2.2 kDa
18
id: quick-cobra-ruby
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.82
65.65
--
2.1 kDa
19
id: gentle-cobra-quartz
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.60
62.64
--
1.8 kDa
15
id: misty-wolf-ruby
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.01
62.05
--
5.7 kDa
50
id: violet-vole-moss
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.72
79.43
--
3.5 kDa
30
id: crimson-eagle-opal
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.03
41.98
--
5.8 kDa
50
id: hollow-shark-sand
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.40
52.05
--
9.5 kDa
80
id: strong-tiger-frost
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.71
53.47
--
2.1 kDa
18
id: young-dove-frost

Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.54
73.95
--
2.1 kDa
19
id: silver-seal-birch
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.46
75.92
--
1.8 kDa
15