Proteins (10)
id: rapid-dove-iron
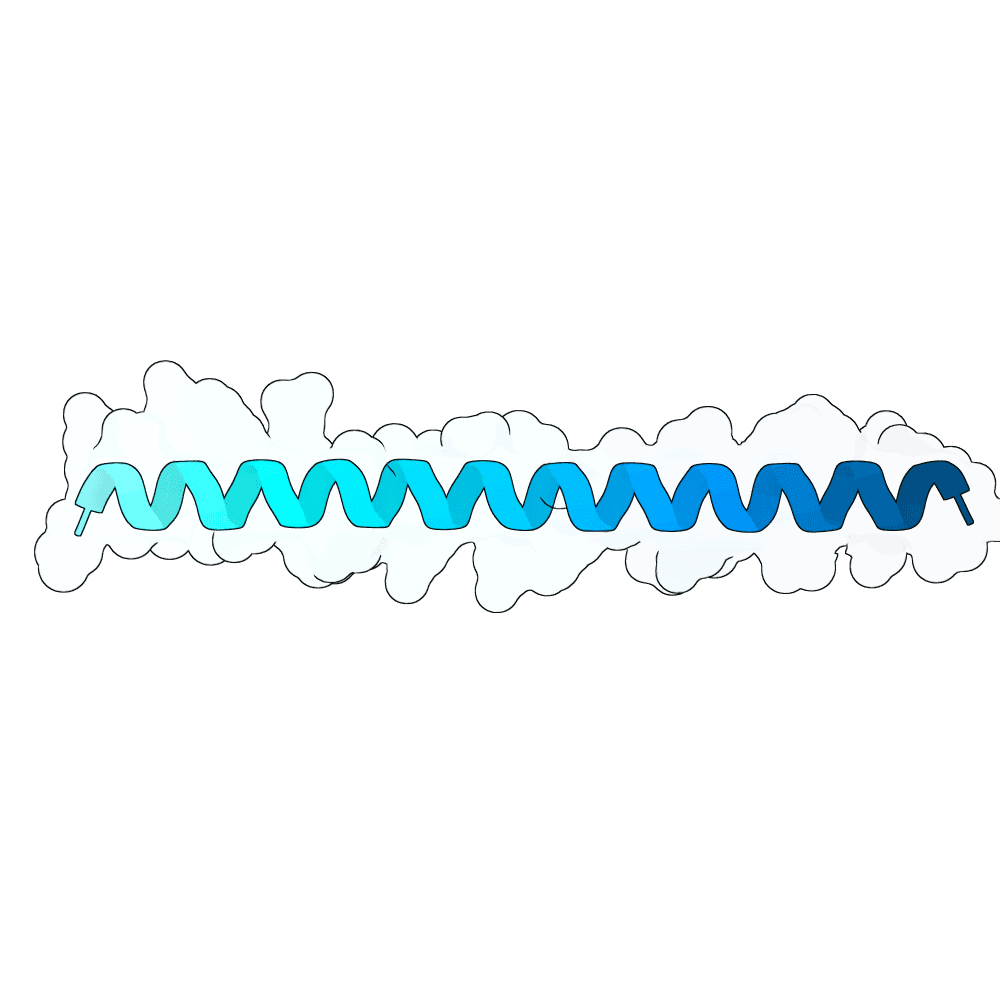
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.66
82.44
--
5.3 kDa
44
id: rough-crane-fern
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.07
84.22
--
5.5 kDa
46
id: azure-cat-ruby
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.52
83.09
--
5.0 kDa
41
id: scarlet-mole-jade
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.39
84.16
--
5.4 kDa
46
id: shy-gecko-maple
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.40
83.15
--
5.8 kDa
48
id: ivory-boar-granite
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.44
82.74
--
5.3 kDa
44
id: small-lynx-willow
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.00
83.50
--
5.5 kDa
46
id: green-bear-lava
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.49
84.13
--
5.1 kDa
42
id: soft-jaguar-opal
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.01
83.91
--
5.5 kDa
47
id: vast-ibis-maple
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.63
83.21
--
5.1 kDa
42