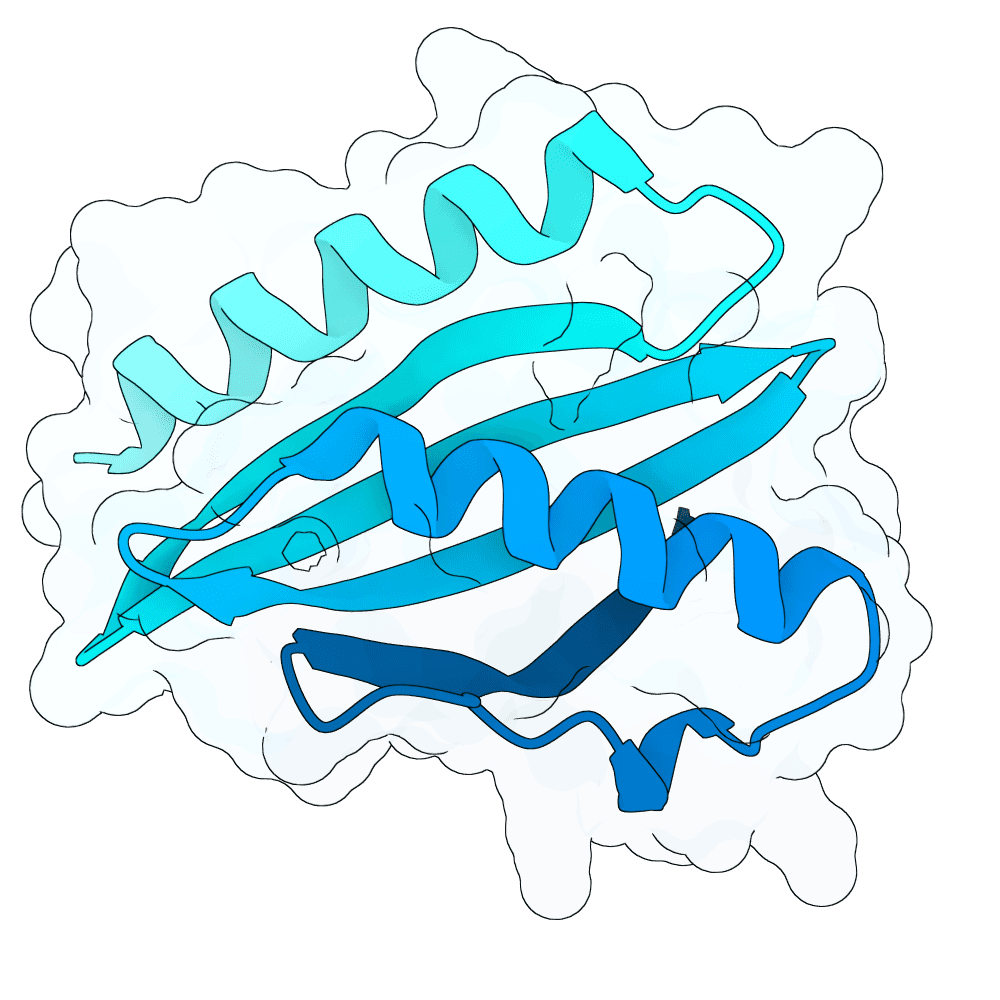
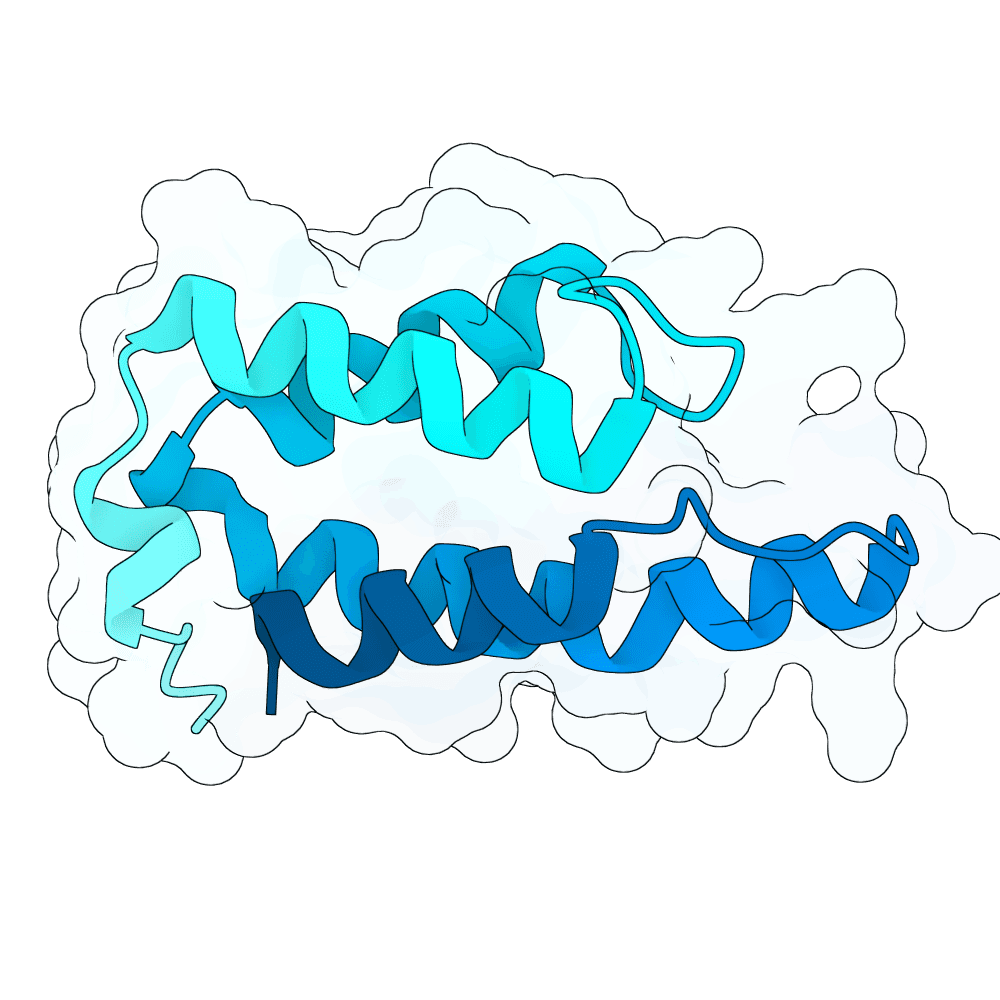
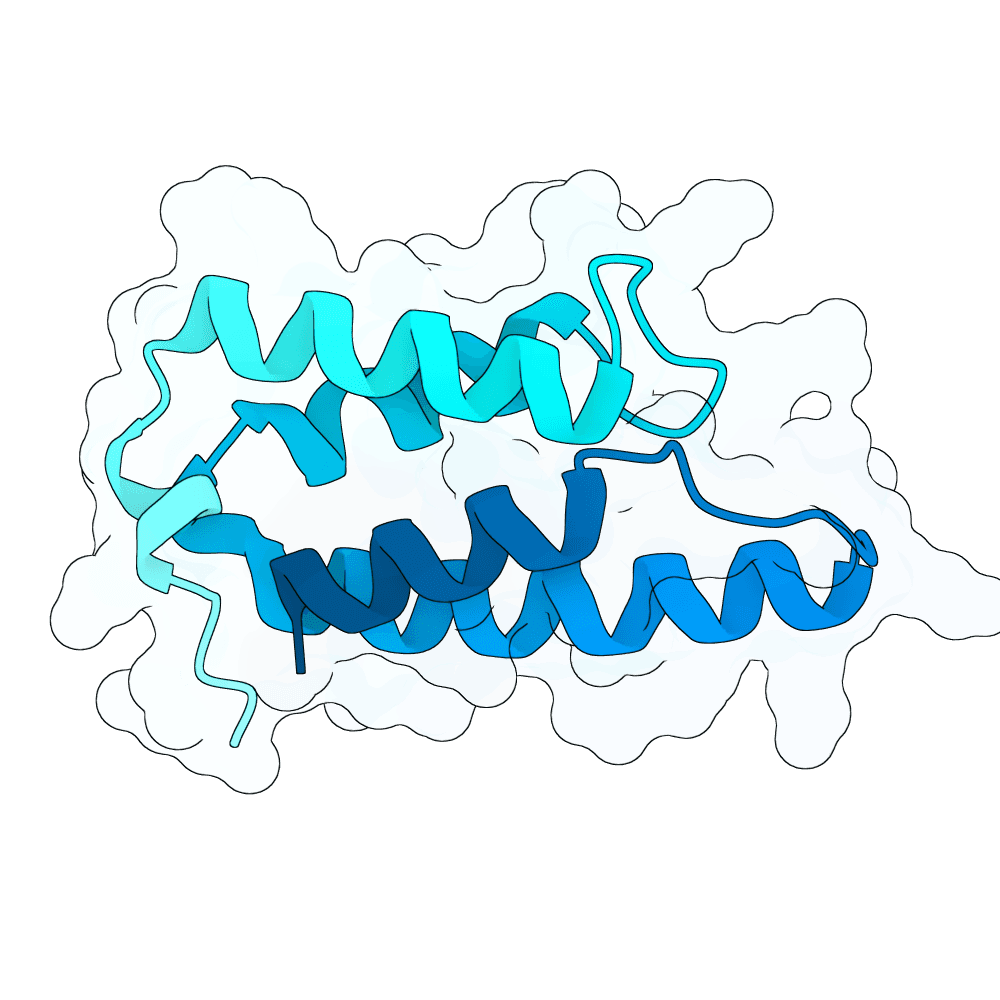
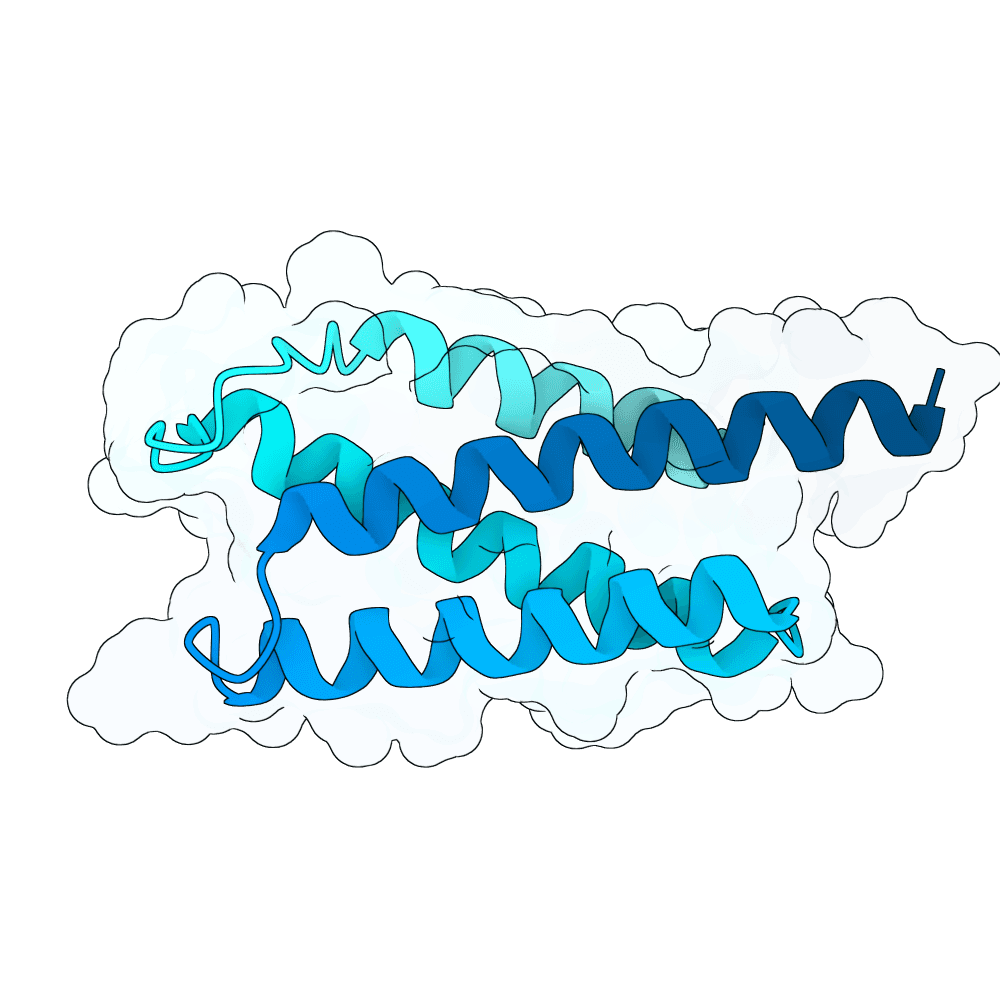
Description
Protein designs were generated using BindCraft, an automated sequence–structure co-design pipeline built on backbone flexiblization and iterative sequence optimization. We employed the 4-stage multimer flexible protocol, which alternates between side-chain redesign and structural relaxation to refine binding-interface geometry while maintaining global fold stability. Designs were screened using BindCraft’s relaxed filter set (relaxed_filters.json), which evaluates metrics such as packing quality, clash score, interface energetics, and secondary-structure agreement, allowing for recovery of diverse but biophysically favorable sequences. Advanced settings from default_4stage_multimer_flexible_hardtarget.json were used to enable flexible backbone sampling around the target hotspot positions. This workflow produced final sequences that are structurally compatible with the input scaffold and predicted to form stable, high-quality interactions with the specified target regions.