Description
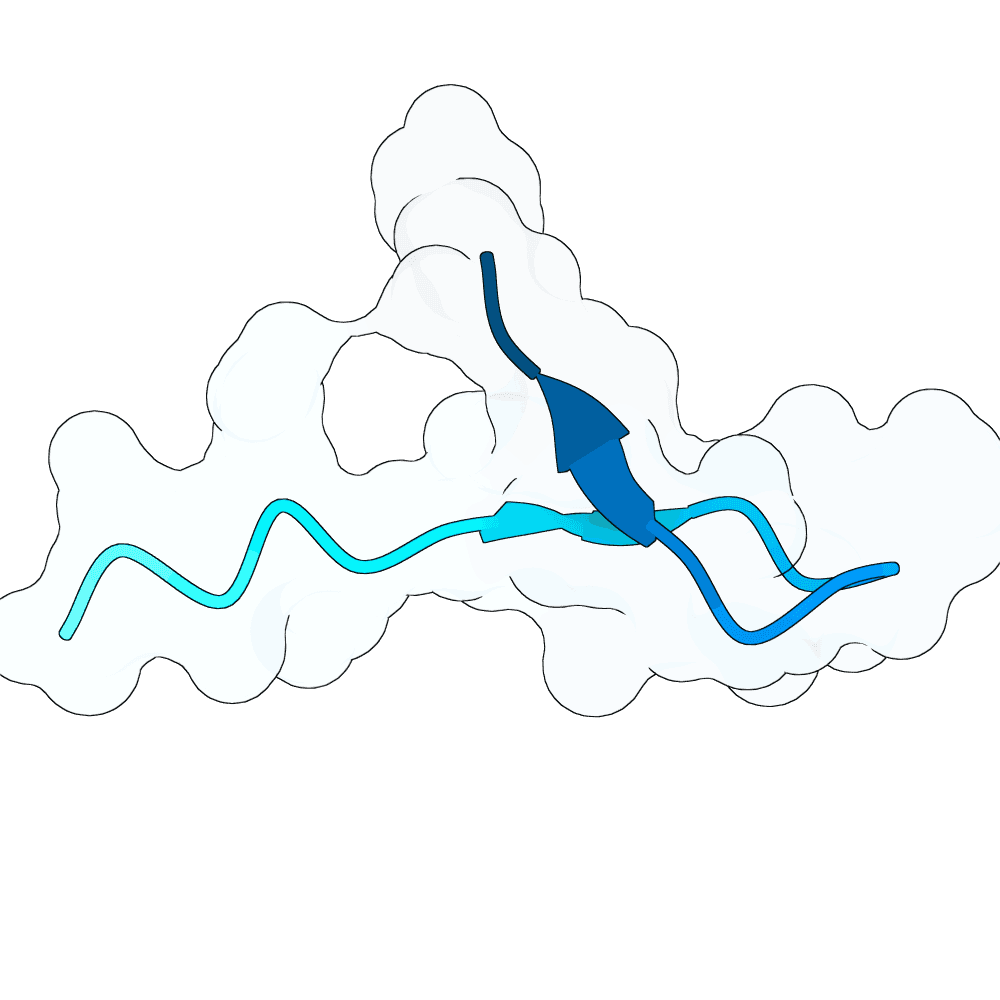
EvoBind (Li, Q., Vlachos, E.N. & Bryant, P. Design of linear and cyclic peptide binders from protein sequence information. Commun Chem 8, 211 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-025-01601-3) was here applied to generate potentially good binders towards the NiV glycoprotein G. The input is the target sequence only. The top scoring designs (lowest loss, distance IF and high plDDT) are predicted to bind the target with a similar interface of the human EB. Notwithstanding the peptide-binder design nature of EvoBind, designing for longer sequences (i.e. 50-80 aa) is also possible. Therefore, through longer iterations, potentially good longer designs were also obtained.