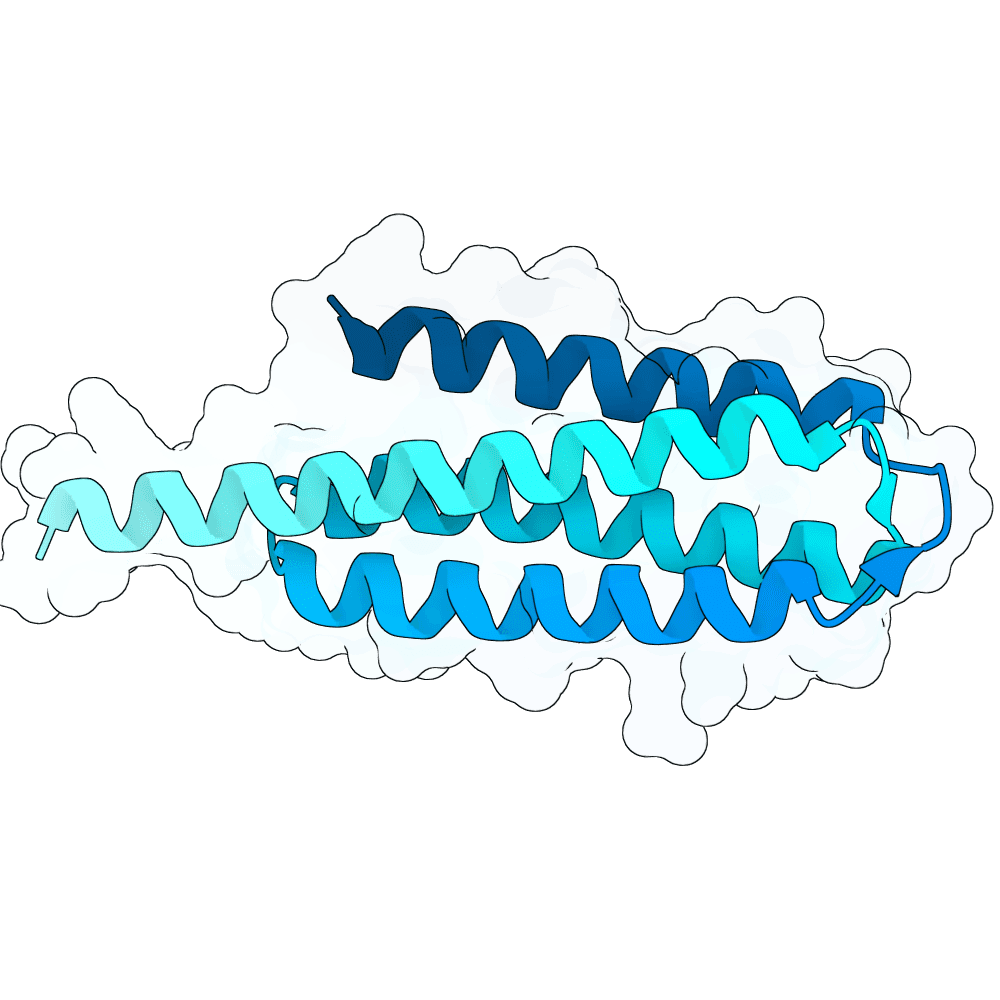
Description
The designs are scaffolds of the experimentally validated binder N237 (https://doi.org/10.64898/2025.12.20.695652). N237 shows low-nanomolar affinity measured by BLI, sub-nanomolar EC50 in ELISA, and in vitro (ELISA-based) competition against both human EphrinB2 and a neutralizing antibody. Validation with infectious Nipah virus was performed in a BSL-4 laboratory, where N237 exhibited weak neutralization compared to the highly potent monoclonal antibody HENV-117.
Based on interface residues of N237 and N101 scaffolds were designed using RFdiffusion1 with ProteinMPNN for sequence generation. Interface residues were excluded from sequence design. In silico validation was performed with Boltz-2 using 50 different seeds. Final submission is composed of designs with average ipSAE over all 50 Boltz-2 predictions <= 0.8.