Proteins (10)
id: brisk-gecko-fern
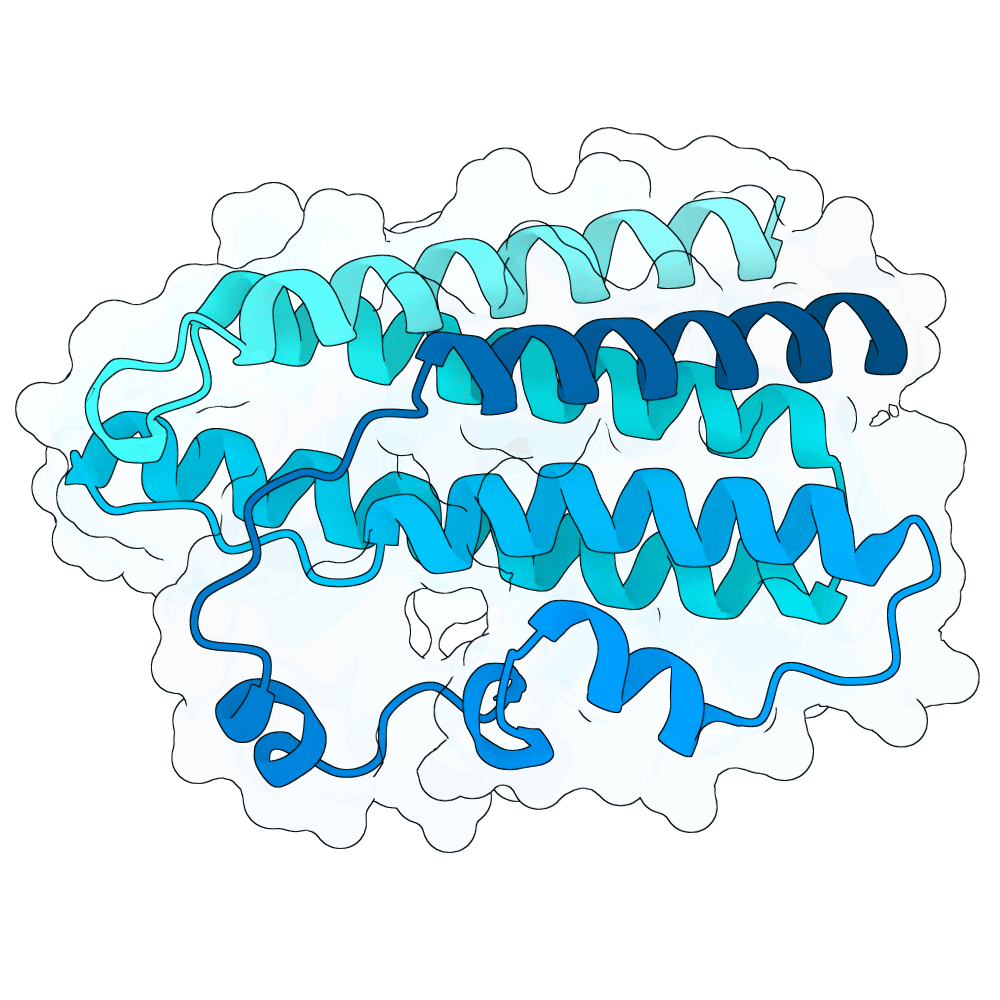
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
None
55.17
True
20.2 kDa
187
id: young-boar-ivy
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
None
82.76
True
10.4 kDa
86
id: scarlet-boar-pine
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
None
41.46
False
15.2 kDa
133
id: hollow-boar-opal
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
None
71.29
True
10.3 kDa
86
id: quiet-wolf-ember
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
None
83.20
True
17.2 kDa
142
id: strong-cat-orchid
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
None
83.09
True
15.1 kDa
128
id: shy-moth-crystal
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
None
56.29
True
15.0 kDa
128
id: scarlet-jaguar-snow
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
None
80.81
True
21.0 kDa
187
id: wild-yak-lava
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
None
84.79
True
20.6 kDa
177
id: solid-bison-willow
Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G
0.36
51.30
--
14.9 kDa
133