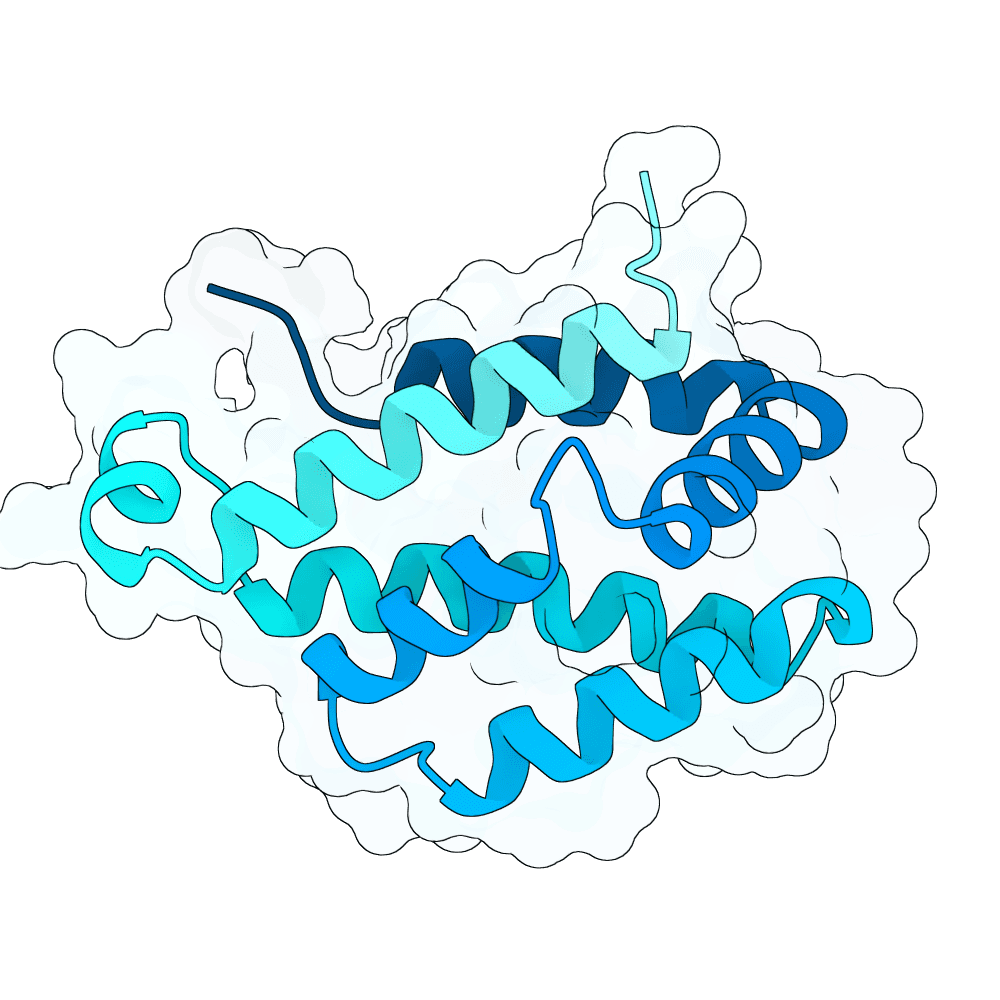
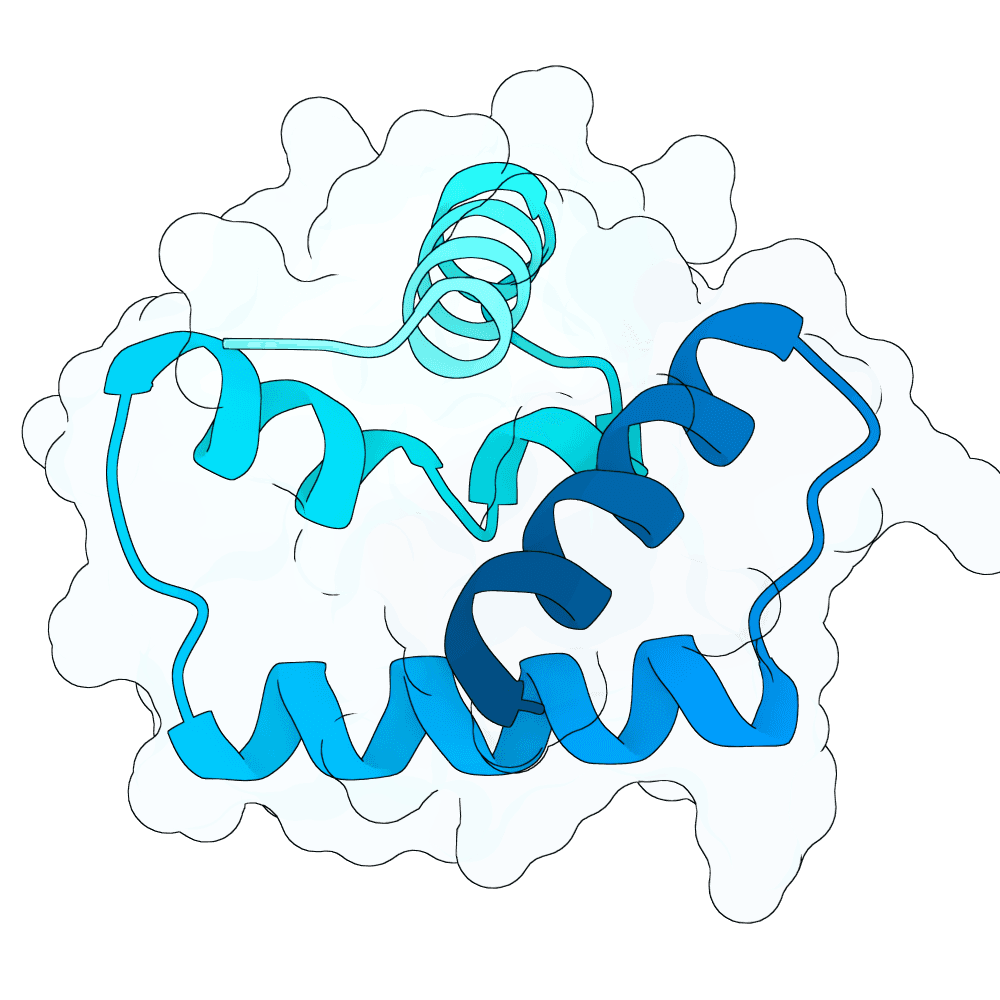
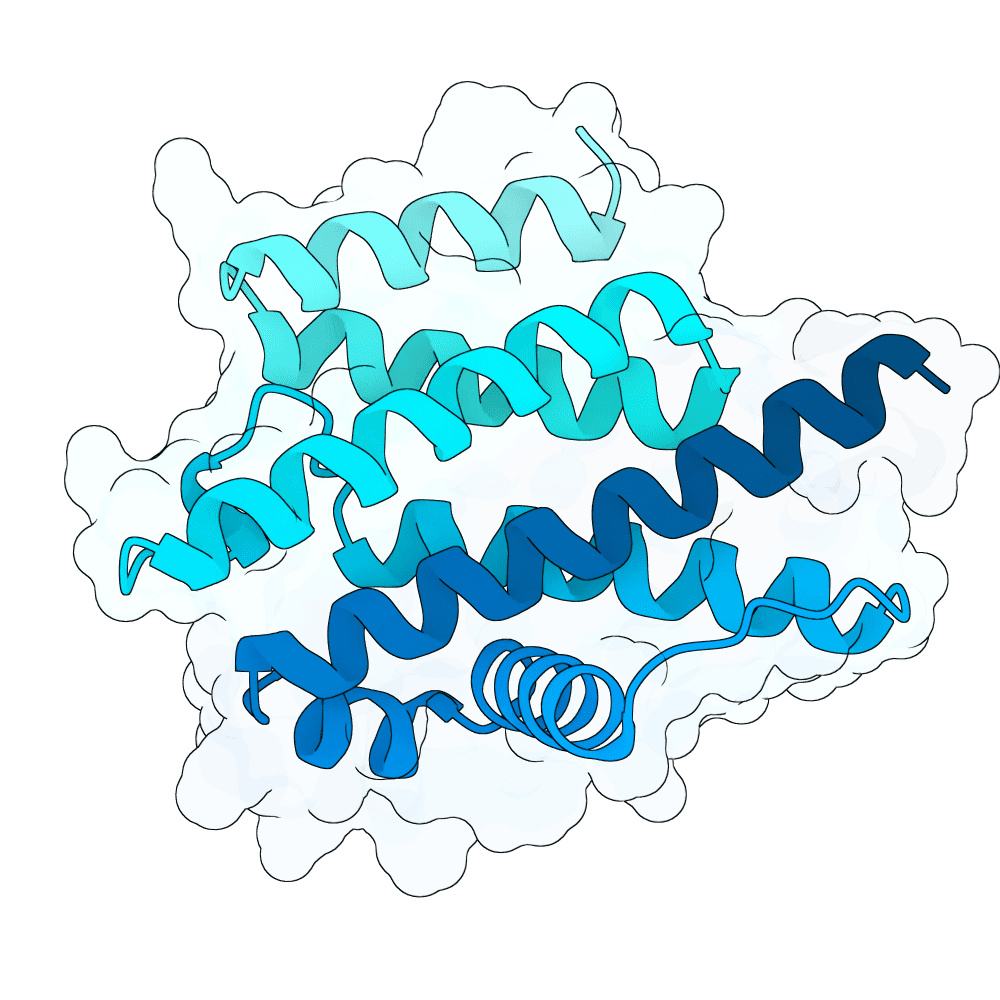
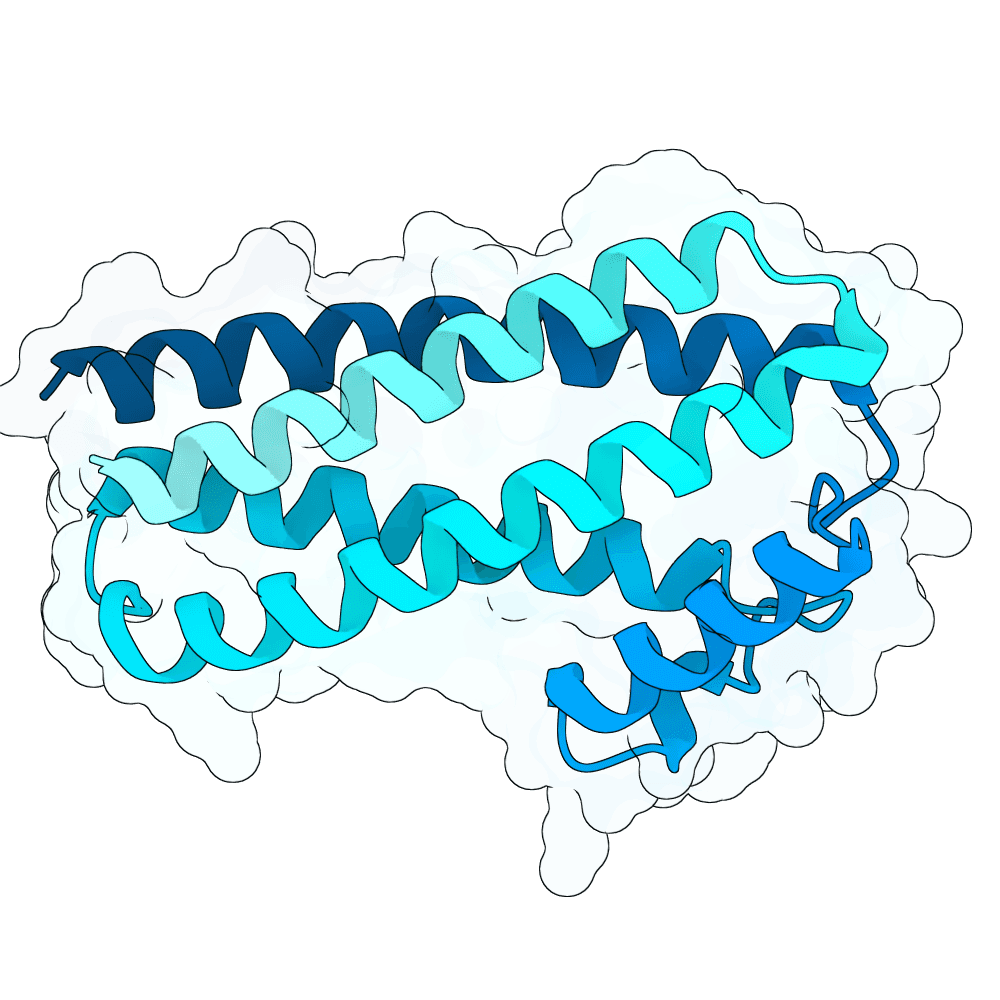
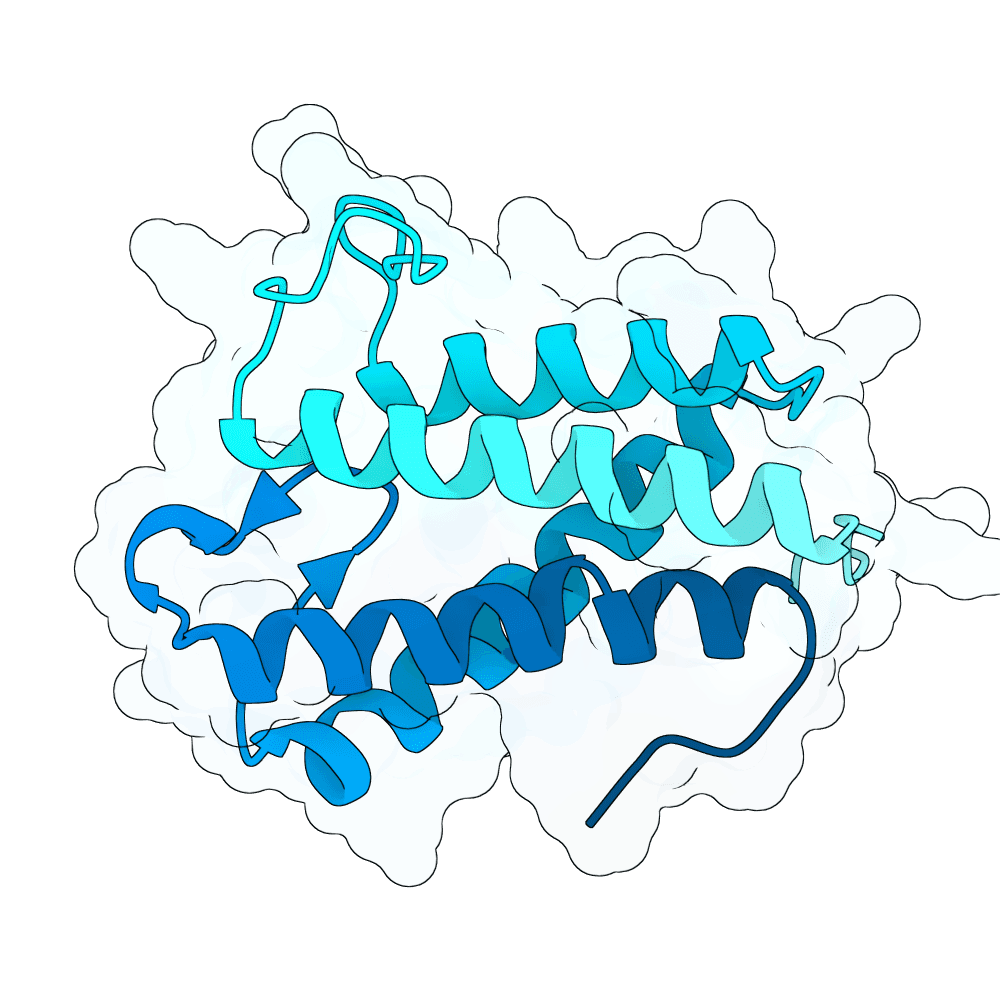
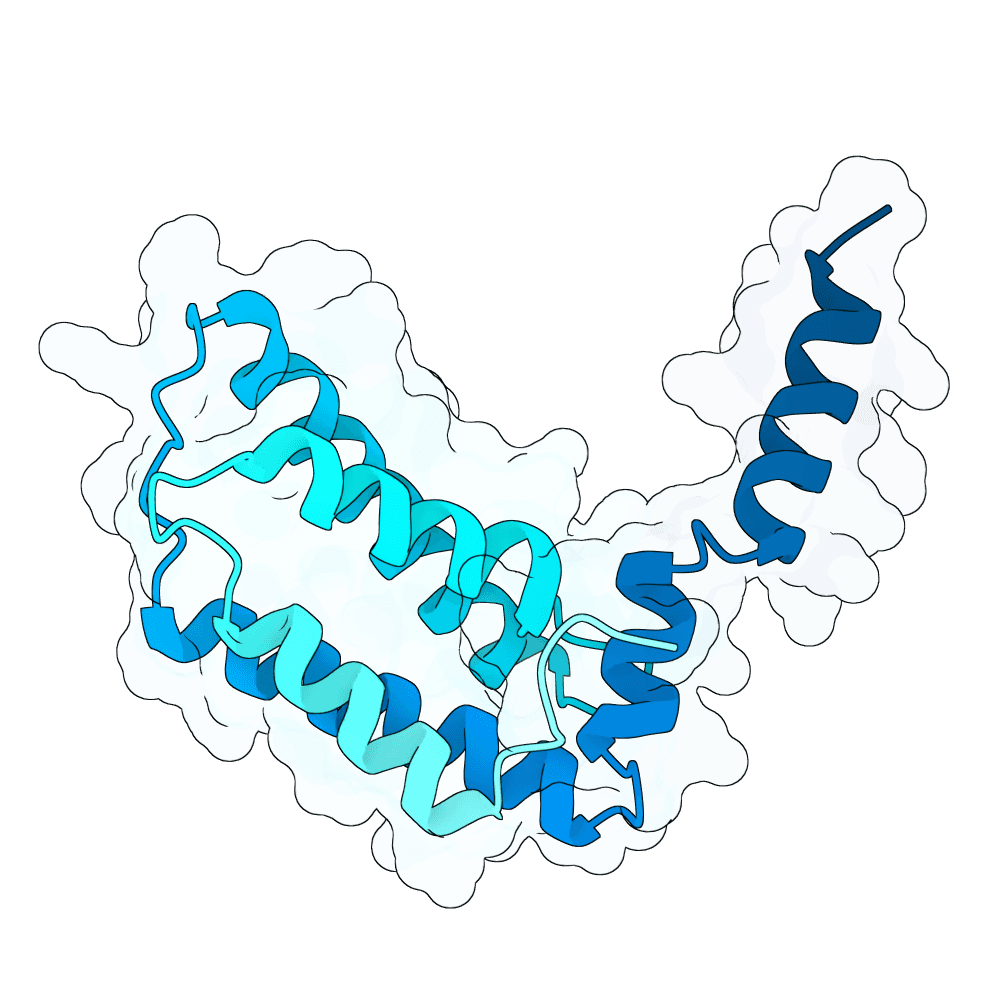
Description
We hypothesized the binder will have better success rate when designed to bind the position where natural binder has contact to, and with a more hydrophobic residue. This method performs de novo binder generation using a four-stage AlphaFold-guided design pipeline procided in Bindcraft. It begins by hallucinating a binder sequence against a chosen target interface using AFDesign, optimizing sequence and structure simultaneously to satisfy hotspot contacts, foldability, and geometric constraints. The top trajectory structures are then evaluated with full AlphaFold-Multimer predictions to obtain reliable confidence and interface metrics. High-quality trajectories are passed to ProteinMPNN for sequence redesign and stabilization, followed by a second AlphaFold-Multimer validation of the redesigned binders. Final designs are scored using structural, energy, and interface metrics (including pLDDT, iPTM, iPAE, dG/dSASA, shape complementarity, packing, and clash checks) to select binders with stable folds and well-defined interfaces.